WHAT IS CATARACT?
- It is clouding (opacification) of the natural lens, which prevents light rays from reaching the retina.
- Early on, a change in glass power may help.
- Later on, it progressively affects vision, till finally, only the perception of light remains.
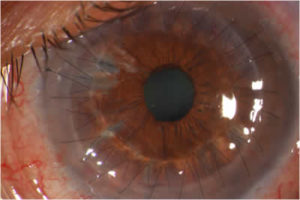
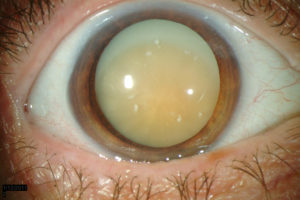
WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS OF CATARACT?
- Painless, gradually progressive blurring of vision.
- Double vision or seeing multiple images.
- Trouble with seeing in poor light conditions and sometimes in excessive sunlight.
- Becoming sensitive to glare, making night driving difficult.
- Difficulty in distance vision and in reading.
WHEN DOES ONE GO IN FOR SURGERY?
- To a large extent is depends on the person undergoing surgery.
- Whenever the cataract affects vision to a degree that it hampers the person’s daily activities (reading, driving, playing golf etc.), surgery should be considered.
- During surgery the normal lens of the eye is removed and replaced with an intra-ocular lens which lasts for the entire lifetime.
SURGICAL OPTIONS
- Surgery can be performed manually through 5- 6 mm wounds called SICS (Small Inscision Cataract Surgery).
- Phacoemulsification is at present universally accepted as the standard of care for cataract surgery.
- Ultrasound energy is used in phacoemulsification to break up the cataract (emulsify) into microscopic fragments which can be sucked out of the eye.
